Summary: Developing a compliant enterprise voice strategy requires strategic planning that balances collaboration needs with security requirements.
- Framework Development: Establish governance policies that define access controls, naming conventions, and lifecycle management for voice-enabled Teams
- Technical Architecture: Design hybrid voice infrastructure that integrates existing systems while meeting compliance standards and performance requirements
- Compliance Integration: Implement retention policies, audit controls, and regulatory measures that satisfy industry-specific requirements like GDPR and HIPAA
- Deployment Strategy: Create phased rollout plans with user training, monitoring capabilities, and ongoing governance to ensure sustained compliance
Structured governance frameworks reduce security risks while enabling faster adoption and more efficient management of enterprise voice systems.
What Makes Enterprise Voice Strategy Critical for Modern Organizations?
Enterprise voice strategy has evolved from simple phone system management to comprehensive communication governance that impacts every aspect of business operations. Microsoft Teams has reached 320 million monthly active users, yet fewer than 10% utilize the platform for external voice communications, representing a significant opportunity for organizations to consolidate their communication infrastructure.
A compliant enterprise voice strategy with Microsoft Teams requires more than technical implementation. It demands a structured approach that addresses regulatory requirements, security protocols, and operational efficiency while maintaining the flexibility that modern businesses need. Organizations without proper voice governance face increased security risks, compliance violations, and operational inefficiencies. Data breaches exposed 7 billion records in just the first half of 2024, with organizations spending an average of $9.36 million per breach in the United States alone.
The complexity of modern enterprise communications means that voice strategy must integrate seamlessly with existing business processes while preparing for future scalability. Pure IP’s enterprise voice solutions provide the foundation for building compliant communication systems that grow with organizational needs.
How Should Organizations Build Their Voice Strategy Foundation?
Creating an effective enterprise voice strategy begins with establishing a comprehensive governance framework that addresses both immediate needs and long-term organizational goals. This foundation determines how voice communications integrate with existing business processes and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
What Are the Core Components of Voice Strategy Governance?
The foundation of any successful enterprise voice strategy rests on five critical governance pillars that work together to create a secure, scalable, and compliant communication environment:
Access Control Framework establishes who can create voice-enabled teams, manage phone numbers, and configure calling policies. This includes defining role-based permissions that align with organizational hierarchy and security requirements. Organizations should implement principle of least privilege access, ensuring users receive only the permissions necessary for their specific job functions.
Naming and Organization Standards create consistent structures that improve user experience and administrative efficiency. These standards should address team naming conventions, channel organization, and phone number assignment protocols. Clear naming conventions help users locate resources quickly while enabling administrators to maintain oversight of the voice environment.
Lifecycle Management Policies define how voice-enabled teams are created, maintained, and decommissioned. This includes establishing criteria for team creation, setting expiration policies for inactive teams, and defining archival procedures that maintain compliance with retention requirements. Automated lifecycle management reduces administrative overhead while ensuring consistent policy enforcement.
Security and Compliance Controls integrate industry-specific regulatory requirements into the voice strategy framework. These controls address data retention, audit logging, encryption standards, and incident response procedures. Organizations must align their voice strategy with existing compliance frameworks while preparing for evolving regulatory landscapes.
User Training and Support Programs ensure successful adoption while maintaining compliance with established policies. Training programs should address both technical functionality and governance requirements, helping users understand not just how to use voice features but why certain policies exist and how to maintain compliance.
How Do You Assess Current Voice Infrastructure Requirements?
Before implementing new voice capabilities, organizations must thoroughly evaluate their existing communication infrastructure to identify integration points, potential conflicts, and upgrade requirements. This assessment provides the foundation for designing a voice architecture that leverages existing investments while addressing identified gaps.
Current System Inventory requires documenting all existing voice technologies, including PBX systems, SIP trunks, analog devices, and third-party applications. This inventory should include technical specifications, user counts, geographic distribution, and integration dependencies. Understanding the current state enables better decision-making about migration strategies and hybrid deployment options.
Network Infrastructure Analysis evaluates whether existing network infrastructure can support enterprise voice requirements. This includes assessing bandwidth capacity, Quality of Service configurations, and network security policies. Voice communications require specific network characteristics to maintain call quality and security standards.
Compliance Requirements Mapping identifies all regulatory and industry-specific requirements that impact voice communications. Different industries face varying compliance obligations, from healthcare’s HIPAA requirements to financial services’ regulatory frameworks. Understanding these requirements early in the planning process prevents costly redesign later in the implementation phase.
What Technical Architecture Considerations Define Success?
Enterprise voice architecture requires careful planning to ensure optimal performance, security, and compliance while supporting current and future business requirements. The technical foundation determines how voice services integrate with existing infrastructure and scale to meet organizational growth.
How Do You Choose the Right Voice Connectivity Option?
Microsoft Teams offers three primary connectivity options for external calling, each with distinct advantages and use cases that align with different organizational requirements and technical capabilities.
Microsoft Calling Plans provide the simplest deployment option for organizations without complex routing requirements. This cloud-based solution includes domestic and international calling plans with Microsoft serving as the PSTN carrier. Organizations choose Calling Plans when they prioritize simplicity over customization and operate primarily in regions where Microsoft provides direct service coverage.
Direct Routing offers maximum flexibility for organizations with complex requirements or existing carrier relationships. This option connects customer-managed Session Border Controllers to Teams Phone, enabling integration with any PSTN provider worldwide. Direct Routing supports advanced call routing, integration with legacy systems, and custom calling policies that align with specific business requirements.
Operator Connect balances simplicity with flexibility by connecting certified carrier services directly through the Microsoft 365 admin center. This option provides easier management than Direct Routing while offering more geographic coverage and cost optimization than Calling Plans. Operator Connect enables organizations to choose providers that best meet their coverage, pricing, and feature requirements.
What Security Architecture Elements Ensure Compliance?
Security architecture for enterprise voice must address multiple layers of protection while maintaining usability and performance. These elements work together to create comprehensive protection against threats while ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
Identity and Access Management forms the foundation of voice security by ensuring only authorized users can access voice capabilities and sensitive communications data. This includes implementing multi-factor authentication, conditional access policies, and regular access reviews. Organizations should integrate voice access controls with existing identity management systems to maintain consistent security policies.
Network Security Controls protect voice traffic during transmission and prevent unauthorized access to communication systems. This includes implementing encryption for all voice communications, network segmentation to isolate voice traffic, and intrusion detection systems that monitor for suspicious activity. Voice communications require specific security considerations due to their real-time nature and potential for eavesdropping.
Data Protection Measures ensure that voice communications and associated metadata receive appropriate protection throughout their lifecycle. This includes implementing retention policies that align with legal requirements, encryption for stored communications, and data loss prevention policies that prevent unauthorized sharing of sensitive information.
Monitoring and Audit Capabilities provide visibility into voice system usage and enable rapid detection of security incidents or compliance violations. Comprehensive logging should capture call metadata, system configuration changes, and user access patterns while protecting privacy and meeting retention requirements.
Which Compliance Requirements Shape Voice Strategy Decisions?
Compliance requirements significantly impact enterprise voice strategy decisions, from technical architecture choices to operational procedures. Organizations must understand how various regulatory frameworks apply to voice communications and design their strategy accordingly.
How Do Industry Regulations Impact Voice Architecture?
Different industries face unique regulatory requirements that directly influence voice architecture decisions and operational procedures. Understanding these requirements early in the planning process ensures that voice systems meet compliance obligations from initial deployment.
Healthcare Organizations operating under HIPAA must implement specific safeguards for voice communications that may contain protected health information. This includes encryption requirements for voice data, access controls that limit who can listen to recordings, and audit logging that tracks all access to voice communications. Healthcare faces average breach costs of $9.77 million between 2022-2024, making robust voice security essential for protecting patient data.
Financial Services face multiple regulatory frameworks including SOX, FINRA, and various international banking regulations that impact voice communications. These requirements often mandate call recording for specific roles, retention periods that may extend for years, and audit capabilities that can reconstruct communication patterns. Financial organizations must also implement controls that prevent insider trading and maintain segregation of duties in voice system administration.
Government and Defense organizations must comply with security frameworks like FedRAMP, FISMA, and specific defense regulations that impact voice system design. These requirements may mandate specific encryption standards, geographic data residency, and security clearance requirements for system administrators. Government voice systems often require air-gapped deployments or specific cloud environment certifications.
Manufacturing and Energy sectors face industry-specific safety and operational requirements that impact voice communications. Emergency communication requirements, integration with industrial control systems, and compliance with safety regulations all influence voice architecture decisions.
What Data Governance Policies Support Voice Compliance?
Data governance policies for voice communications must address the entire lifecycle of voice data while meeting specific regulatory requirements and organizational policies. These policies ensure that voice communications receive appropriate protection and handling throughout their existence.
Retention and Deletion Policies define how long voice communications and associated metadata must be preserved and when they should be deleted. These policies must balance legal requirements for evidence preservation with privacy obligations and storage cost considerations. Organizations should implement automated retention policies that ensure consistent application while reducing administrative overhead.
Classification and Labeling Systems help organizations identify sensitive voice communications and apply appropriate protection measures. This includes implementing sensitivity labels that automatically apply encryption and access controls based on communication content or participants. Classification systems should integrate with existing data governance frameworks to maintain consistency across all organizational data types.
Cross-Border Data Transfer Controls ensure that voice communications comply with regulations like GDPR when data crosses international boundaries. Organizations with global operations must understand data residency requirements and implement technical controls that ensure compliance while maintaining operational efficiency.
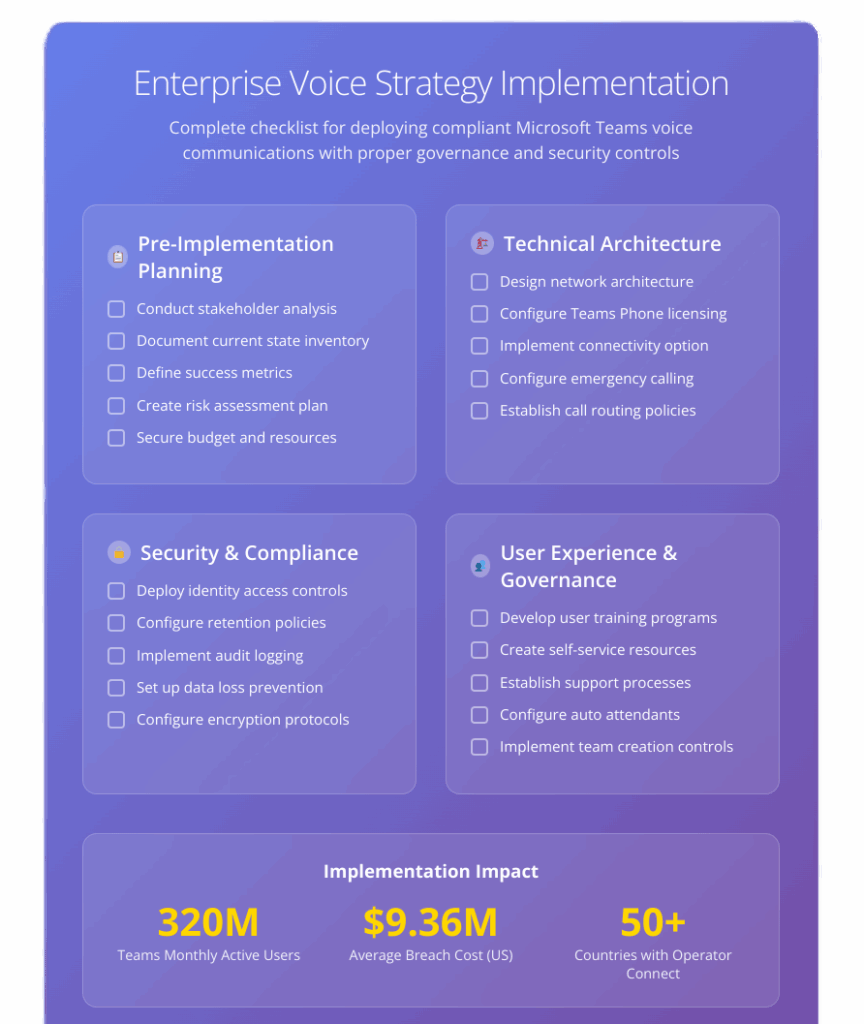
Enterprise Voice Strategy Implementation Checklist
Successful enterprise voice strategy implementation requires systematic execution of technical, governance, and operational elements. This comprehensive checklist ensures that all critical aspects receive proper attention during deployment.
Pre-Implementation Planning
- Conduct stakeholder analysis identifying all departments and roles affected by voice implementation
- Document current state inventory including existing voice systems, network infrastructure, and compliance requirements
- Define success metrics establishing measurable goals for adoption, compliance, and operational efficiency
- Establish project governance structure with clear roles, responsibilities, and decision-making authority
- Create risk assessment and mitigation plan addressing technical, security, and compliance risks
- Develop communication plan for informing stakeholders about changes and timeline
- Secure necessary budget and resources including licensing, infrastructure, and professional services
Technical Architecture Setup
- Design network architecture ensuring adequate bandwidth and Quality of Service configuration
- Configure Teams Phone licensing for all voice-enabled users according to role requirements
- Implement chosen connectivity option (Calling Plans, Direct Routing, or Operator Connect)
- Set up Session Border Controllers if using Direct Routing for external connectivity
- Configure emergency calling including location services and emergency routing policies
- Establish call routing policies defining how calls flow through the organization
- Implement monitoring and analytics tools for tracking system performance and usage
Security and Compliance Configuration
- Deploy identity and access controls including multi-factor authentication and conditional access
- Configure retention policies that meet legal and regulatory requirements for voice communications
- Implement audit logging to track system usage and changes for compliance reporting
- Set up data loss prevention policies to prevent unauthorized sharing of sensitive communications
- Configure encryption for voice traffic and stored communications data
- Establish incident response procedures specifically for voice communication security events
- [ ] Create compliance reporting processes for regular auditing and regulatory submissions
User Experience and Adoption
- Develop user training programs covering both functionality and compliance requirements
- Create self-service resources including documentation and video tutorials
- Establish support processes for voice-related technical issues and questions
- Configure auto attendants and call queues to improve caller experience
- Set up voicemail and call forwarding policies that meet business requirements
- Deploy desk phones or headsets as needed for user roles and preferences
- Conduct pilot testing with select user groups before full deployment
Governance and Ongoing Management
- Implement team creation controls that enforce naming conventions and approval processes
- Configure lifecycle management including automatic archiving of inactive teams
- Establish regular review processes for access permissions and compliance policies
- Create performance monitoring dashboards for tracking adoption and system health
- Set up automated compliance checks to identify policy violations or configuration drift
- Develop change management procedures for updating policies and technical configurations
- Plan regular training updates to keep users informed of new features and policy changes
What Governance Best Practices Ensure Long-Term Success?
Effective governance extends beyond initial implementation to create sustainable processes that adapt to changing business requirements while maintaining compliance and security standards. These practices ensure that voice strategy remains aligned with organizational goals over time.
How Do You Maintain Compliance Over Time?
Maintaining compliance requires ongoing attention to evolving regulations, changing business requirements, and system updates that may impact existing policies. Organizations must establish processes that proactively identify and address compliance gaps before they become violations.
Regular Compliance Auditing should occur on scheduled intervals with both automated and manual review processes. Automated auditing can identify configuration drift, policy violations, and unusual usage patterns that may indicate security issues or compliance problems. Manual auditing provides deeper analysis of complex scenarios and validates that automated systems function correctly.
Policy Update Procedures ensure that governance policies evolve with changing regulations and business requirements. This includes establishing processes for reviewing regulatory changes, assessing their impact on existing policies, and implementing necessary updates. Organizations should maintain documentation of policy changes and their rationale to support compliance auditing and training efforts.
User Access Reviews verify that voice permissions remain appropriate as user roles change within the organization. Regular access reviews help identify permissions that are no longer needed and ensure that new users receive appropriate access levels. These reviews should include both technical permissions and business process access to maintain comprehensive oversight.
Incident Response and Remediation processes address compliance violations quickly and thoroughly. This includes procedures for investigating potential violations, implementing corrective actions, and preventing similar issues in the future. Organizations should maintain documentation of all compliance incidents to support regulatory reporting and demonstrate good faith compliance efforts.
What Integration Strategies Support Hybrid Voice Environments?
Many organizations operate hybrid voice environments that combine cloud-based Teams calling with legacy systems and third-party applications. Successful integration requires careful planning to maintain security and compliance across all systems while providing seamless user experience.
Legacy System Integration enables organizations to maintain existing investments while transitioning to modern voice capabilities. This may include integrating existing PBX systems through Direct Routing or maintaining analog devices through gateway solutions. Organizations can also mix Operator Connect with Direct Routing to address different requirements across locations while maintaining centralized management.
Third-Party Application Integration connects voice capabilities with existing business applications like CRM systems, help desk platforms, and workflow automation tools. These integrations can improve productivity by enabling click-to-call functionality and automatic call logging. Organizations should evaluate integration security and ensure that third-party connections meet compliance requirements.
Multi-Platform Coordination addresses organizations that use multiple communication platforms for different business functions. This includes ensuring consistent governance policies across platforms and maintaining audit capabilities that provide comprehensive visibility into all voice communications. Coordination efforts should focus on user experience consistency while maintaining security boundaries. Organizations can achieve global coverage through strategic provider selection and hybrid deployment strategies.
Gradual Migration Strategies enable organizations to transition from legacy systems to Teams-based voice communications without disrupting business operations. Successful migration requires careful planning of user groups, timing coordination, and fallback procedures. Organizations should prioritize maintaining communication capabilities throughout the transition process while ensuring that security and compliance measures remain effective.

How Do You Design Effective Teams Compliance Programs?
Teams compliance programs require comprehensive frameworks that address technical controls, user behavior, and organizational processes. These programs ensure that Microsoft Teams usage aligns with regulatory requirements while supporting business objectives.
What Technical Controls Enable Compliance Automation?
Technical controls provide the foundation for compliance automation by implementing policies that automatically enforce requirements without requiring constant user attention. These controls reduce compliance risks while minimizing administrative overhead.
Automated Retention Policies ensure that voice communications and associated data receive appropriate lifecycle management based on content type, business function, and regulatory requirements. These policies can automatically preserve important communications while deleting data that has reached the end of its retention period. Organizations should configure retention policies that align with legal requirements while optimizing storage costs.
Sensitivity Labels and Data Classification automatically apply protection measures based on communication content and context. This includes implementing labels that trigger encryption, access restrictions, and audit logging for sensitive communications. Classification systems should integrate with existing data governance frameworks to provide consistent protection across all organizational systems.
Compliance Communication Controls monitor voice communications for regulatory violations, inappropriate content, and security threats. These controls can automatically flag potential issues for human review while maintaining privacy protections. Organizations should carefully configure communication controls to balance compliance requirements with employee privacy expectations. Nearly 64% of organizations lack full visibility into their AI and communication risks, highlighting the importance of comprehensive monitoring solutions.
Audit and Monitoring Automation provides continuous oversight of voice system usage and configuration. Automated monitoring can identify configuration drift, unusual usage patterns, and potential security incidents without requiring constant human attention. Organizations should implement monitoring that provides actionable alerts while avoiding alert fatigue.
How Do You Integrate Voice Architecture with Existing Security Frameworks?
Voice architecture must integrate seamlessly with existing organizational security frameworks to maintain consistent protection across all systems while supporting compliance requirements. This integration ensures that voice communications receive appropriate security controls without creating operational friction.
Identity Integration connects voice access controls with existing identity management systems to provide consistent authentication and authorization across all organizational systems. This includes implementing single sign-on capabilities and ensuring that voice permissions align with user roles and responsibilities. Identity integration should support both user convenience and security policy enforcement.
Network Security Integration ensures that voice communications receive appropriate protection from existing network security controls including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and network monitoring tools. Voice traffic may require specific security configurations due to its real-time nature and quality requirements. Organizations should implement security controls that protect voice communications without degrading performance.
Data Security Integration applies existing data protection policies to voice communications and associated metadata. This includes implementing encryption standards, access controls, and data loss prevention measures that align with organizational data classification policies. Data security integration should provide consistent protection while accommodating the unique characteristics of voice communications.
Incident Response Integration ensures that voice-related security incidents receive appropriate attention within existing incident response procedures. This includes configuring monitoring tools to detect voice-specific threats and ensuring that incident response teams understand voice system architecture and potential attack vectors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What licensing requirements are needed for compliant enterprise voice strategy? Enterprise voice implementation requires Microsoft Teams Phone licenses for all voice-enabled users, plus appropriate calling plan licenses or Direct Routing infrastructure depending on your connectivity choice. Organizations should also consider compliance-specific licensing for features like communication compliance monitoring and advanced audit capabilities. Licensing costs vary based on user count, calling requirements, and compliance feature needs.
How long does typical enterprise voice strategy implementation take? Implementation timelines range from 3-6 months for straightforward deployments to 12-18 months for complex organizations with extensive compliance requirements and legacy system integration needs. The timeline depends on factors including organizational size, technical complexity, compliance requirements, and change management processes. Phased implementations often provide faster time-to-value while reducing risk.
What are the most common compliance challenges during voice deployment? Common compliance challenges include ensuring proper data retention across multiple systems, maintaining audit trails for voice communications, implementing appropriate access controls for sensitive communications, and integrating voice governance with existing compliance frameworks. Organizations also struggle with balancing compliance requirements against user experience and operational efficiency. Proper planning and expert guidance help address these challenges proactively.
How do you ensure voice quality while maintaining security compliance? Voice quality and security compliance can be achieved simultaneously through proper network design, Quality of Service configuration, and security controls that accommodate real-time communication requirements. This includes implementing encryption that doesn’t significantly impact latency, configuring firewall rules that prioritize voice traffic, and using security tools designed for real-time communications. Regular monitoring helps identify and resolve conflicts between quality and security requirements.
What ongoing costs should organizations budget for enterprise voice strategy? Ongoing costs include Microsoft licensing fees, PSTN connectivity charges, network infrastructure maintenance, compliance monitoring tools, and administrative overhead for governance and support. Organizations should budget for regular compliance auditing, user training updates, and system upgrades that maintain security and functionality. Cost optimization strategies include right-sizing licensing, implementing automated governance controls, and choosing connectivity options that align with usage patterns.
Ready to Transform Your Enterprise Voice Communications?
Creating a compliant enterprise voice strategy with Microsoft Teams requires systematic planning that addresses technical architecture, governance frameworks, and ongoing compliance management. Organizations that invest in comprehensive voice governance see improved security, better user adoption, and reduced compliance risks while enabling the collaboration capabilities that drive business success.
The key to success lies in balancing security requirements with user experience, implementing automated controls that reduce administrative overhead, and establishing governance processes that adapt to changing business and regulatory requirements. Enterprise voice strategy isn’t just about technology implementation—it’s about creating sustainable communication systems that support organizational goals while protecting sensitive information and maintaining compliance obligations.
Ready to build a compliant enterprise voice strategy that scales with your organization? Contact Pure IP today to discover how our enterprise voice solutions can help you achieve your communication goals while maintaining the highest standards of security and compliance.





